The discussion in the previous section about the use of fiscal policy to close gaps suggests that economies can be easily stabilized by government actions to shift the aggregate demand curve. However, as we discovered with monetary policy in the previous chapter, government attempts at stabilization are fraught with difficulties.
Discretionary fiscal policy is subject to the same lags that we discussed for monetary policy. It takes some time for policy makers to realize that a recessionary or an inflationary gap exists—the recognition lag. Recognition lags stem largely from the difficulty of collecting economic data in a timely and accurate fashion. The current recession was not identified until October 2008, when the Business Cycle Dating Committee of the National Bureau of Economic Research announced that it had begun in December 2007. Then, more time elapses before a fiscal policy, such as a change in government purchases or a change in taxes, is agreed to and put into effect—the implementation lag. Finally, still more time goes by before the policy has its full effect on aggregate demand—the impact lag.
Changes in fiscal policy are likely to involve a particularly long implementation lag. A tax cut was proposed to presidential candidate John F. Kennedy in 1960 as a means of ending the recession that year. He recommended it to Congress in 1962. It was not passed until 1964, three years after the recession had ended. Some economists have concluded that the long implementation lag for discretionary fiscal policy makes this stabilization tool ineffective. Fortunately, automatic stabilizers respond automatically to changes in the economy. They thus avoid not only the implementation lag but also the recognition lag.
The implementation lag results partly from the nature of bureaucracy itself. The CBO estimate that only a portion of the spending for the stimulus plan passed in 2009 will be spent in the next two years is an example of the implementation lag. Government spending requires bureaucratic approval of that spending. For example, a portion of the stimulus plan must go through the Department of Energy. One division of the department focuses on approving loan guarantees for energy-saving industrial projects. It was created early in 2007 as part of another effort to stimulate economic activity. A Minnesota company, Sage Electrochromics, has developed a process for producing windows that can be darkened or lightened on demand to reduce energy use in buildings. Sage applied two years ago for a guarantee on a loan of $66 million to build a plant that would employ 250 workers. Its application has not been approved. In fact, the loan approval division, which will be crucial for projects in the stimulus plan, has never approved any application made to it in its two years in existence!
Energy Secretary Steven Chu, a Nobel Prize-winning physicist, recognizes the urgency of the problem. In an interview with the Wall Street Journal, Dr. Chu said that his agency would have to do better. “Otherwise, it’s just going to be a bust,” he said (Power & King Jr., 2009).
Because an expansionary fiscal policy either increases government spending or reduces revenues, it increases the government budget deficit or reduces the surplus. A contractionary policy is likely to reduce a deficit or increase a surplus. In either case, fiscal policy thus affects the bond market. Our analysis of monetary policy showed that developments in the bond market can affect investment and net exports. We shall find in this section that the same is true for fiscal policy.
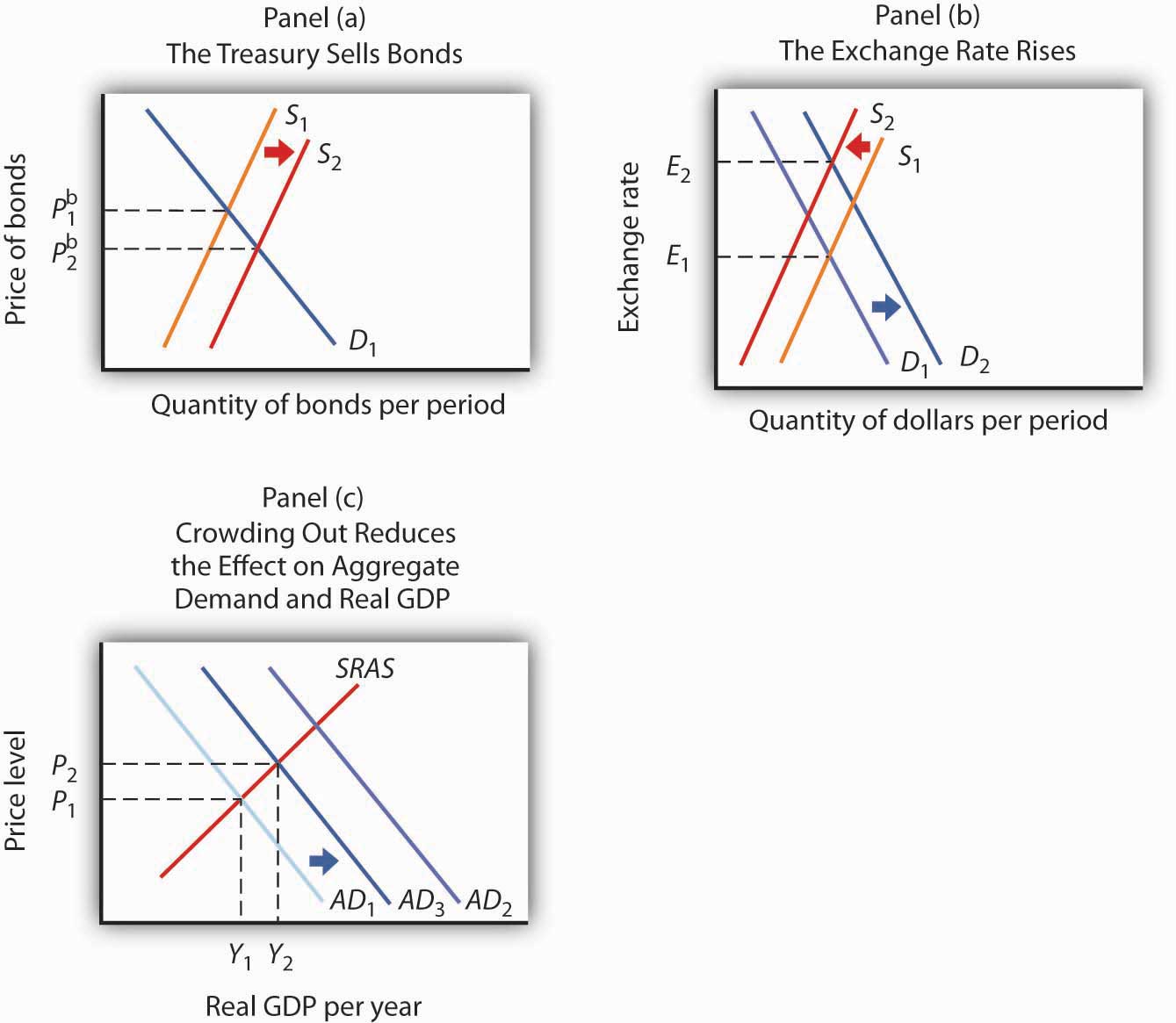
Figure 12.10 “An Expansionary Fiscal Policy and Crowding Out” shows the impact of an expansionary fiscal policy: an increase in government purchases. The increase in government purchases increases the deficit or reduces the surplus. In either case, the Treasury will sell more bonds than it would have otherwise, shifting the supply curve for bonds to the right in Panel (a). That reduces the price of bonds, raising the interest rate. The increase in the interest rate reduces the quantity of private investment demanded. The higher interest rate increases the demand for and reduces the supply of dollars in the foreign exchange market, raising the exchange rate in Panel (b). A higher exchange rate reduces net exports. Panel (c) shows the effects of all these changes on the aggregate demand curve. Before the change in government purchases, the economy is in equilibrium at a real GDP of Y1, determined by the intersection of AD1 and the short-run aggregate supply curve. The increase in government expenditures would shift the curve outward to AD2 if there were no adverse impact on investment and net exports. But the reduction in investment and net exports partially offsets this increase. Taking the reduction in investment and net exports into account means that the aggregate demand curve shifts only to AD3. The tendency for an expansionary fiscal policy to reduce other components of aggregate demand is called crowding out . In the short run, this policy leads to an increase in real GDP to Y2 and a higher price level, P2.
Figure 12.10 An Expansionary Fiscal Policy and Crowding Out

In Panel (a), increased government purchases are financed through the sale of bonds, lowering their price to P b 2. In Panel (b), the higher interest rate causes the exchange rate to rise, reducing net exports. Increased government purchases would shift the aggregate demand curve to AD2 in Panel (c) if there were no crowding out. Crowding out of investment and net exports, however, causes the aggregate demand curve to shift only to AD3. Then a higher price level means that GDP rises only to Y2.
Crowding out reduces the effectiveness of any expansionary fiscal policy, whether it be an increase in government purchases, an increase in transfer payments, or a reduction in income taxes. Each of these policies increases the deficit and thus increases government borrowing. The supply of bonds increases, interest rates rise, investment falls, the exchange rate rises, and net exports fall.
Note, however, that it is private investment that is crowded out. The expansionary fiscal policy could take the form of an increase in the investment component of government purchases. As we have learned, some government purchases are for goods, such as office supplies, and services. But the government can also purchase investment items, such as roads and schools. In that case, government investment may be crowding out private investment.
The reverse of crowding out occurs with a contractionary fiscal policy—a cut in government purchases or transfer payments, or an increase in taxes. Such policies reduce the deficit (or increase the surplus) and thus reduce government borrowing, shifting the supply curve for bonds to the left. Interest rates drop, inducing a greater quantity of investment. Lower interest rates also reduce the demand for and increase the supply of dollars, lowering the exchange rate and boosting net exports. This phenomenon is known as “ crowding in .”
Crowding out and crowding in clearly weaken the impact of fiscal policy. An expansionary fiscal policy has less punch; a contractionary policy puts less of a damper on economic activity. Some economists argue that these forces are so powerful that a change in fiscal policy will have no effect on aggregate demand. Because empirical studies have been inconclusive, the extent of crowding out (and its reverse) remains a very controversial area of study.
Also, the fact that government deficits today may reduce the capital stock that would otherwise be available to future generations does not imply that such deficits are wrong. If, for example, the deficits are used to finance public sector investment, then the reduction in private capital provided to the future is offset by the increased provision of public sector capital. Future generations may have fewer office buildings but more schools.
Suppose Congress and the president agree that something needs to be done to close a recessionary gap. We have learned that fiscal policies that increase government purchases, reduce taxes, or increase transfer payments—or do a combination of these—all have the potential, theoretically, to raise real GDP. The government must decide which kind of fiscal policy to employ. Because the decision makers who determine fiscal policy are all elected politicians, the choice among the policy options available is an intensely political matter, often reflecting the ideology of the politicians.
For example, those who believe that government is too big would argue for tax cuts to close recessionary gaps and for spending cuts to close inflationary gaps. Those who believe that the private sector has failed to provide adequately a host of services that would benefit society, such as better education or public transportation systems, tend to advocate increases in government purchases to close recessionary gaps and tax increases to close inflationary gaps.
Another area of contention comes from those who believe that fiscal policy should be constructed primarily so as to promote long-term growth. Supply-side economics is the school of thought that promotes the use of fiscal policy to stimulate long-run aggregate supply. Supply-side economists advocate reducing tax rates in order to encourage people to work more or more individuals to work and providing investment tax credits to stimulate capital formation.
While there is considerable debate over how strong the supply-side effects are in relation to the demand-side effects, such considerations may affect the choice of policies. Supply-siders tend to favor tax cuts over increases in government purchases or increases in transfer payments. President Reagan advocated tax cuts in 1981 on the basis of their supply-side effects. Coupled with increased defense spending in the early 1980s, fiscal policy under Mr. Reagan clearly stimulated aggregate demand by increasing both consumption and investment. Falling inflation and accelerated growth are signs that supply-side factors may also have been at work during that period. President George W. Bush’s chief economic adviser, N. Gregory Mankiw, argued that the Bush tax cuts would encourage economic growth, a supply-side argument. Mr. Bush’s next chief economic adviser, Ben Bernanke, who became the next chairman of the Federal Reserve Board in 2006, made a similar argument and urged that the Bush tax cuts be made permanent.
Finally, even when there is agreement to stimulate the economy, say through increasing government expenditures on highways, the how question remains. How should the expenditures be allocated? Specifically, which states should the highways run through? Each member of Congress has a political stake in the outcome. These types of considerations make the implementation lag particularly long for fiscal policy.
Do the following hypothetical situations tend to enhance or make more difficult the use of fiscal policy as a stabilization tool?

In an intriguing study, economist Baotai Wang examined the degree of crowding out of Canadian private investment as a result of government expenditures from 1961–2000. What made Professor Wang’s analysis unusual was that he divided Canadian government expenditures into five categories: expenditures for health and education, expenditures for capital and infrastructure, expenditures for the protection of persons and property (which included defense spending), expenditures for debt services, and expenditures for government and social services.
Mr. Wang found that only government expenditures for capital and infrastructure crowded out private investment. While these expenditures reduced private investment, they represented increased public sector investment for things such as highways and ports.
Expenditures for health and education actually “crowded in” private sector investment. These expenditures, Mr. Wang argued, represented increases in human capital. Such increases complement returns on private sector investment and therefore increase it.
Mr. Wang found that Canadian government expenditures for debt service, the protection of persons and property, and for government and social services had no effect on private sector investment. He argued that expenditures for protection of persons and property may involve some crowding out, but that they also stimulated private investment by firms winning government contracts for defense purchases. The same explanation could be applied to government expenditures for government and social services. These also include an element of investment in human capital.
His results suggest that crowding out depends on the nature of spending done by the government. Some kinds of spending clearly did not crowd out private sector investment in Canada.
Source: Baotai Wang, “Effects of Government Expenditure on Private Investment: Canadian Empirical Evidence,” Empirical Economics 30, no. 2 (September 2005): 493–504.
Power, S. and Neil King, Jr., “Next Challenge on Stimulus: Spending All That Money,” Wall Street Journal, February 13, 2009, p. A1.